The sealed-for-life deep groove ball type bearings are some of the most commonly used bearings in rotary valves. Grease filled bearings that are sealed using neoprene or similar seals are appropriate for temperatures up to 300℃ for high temperature applications. The bearings’ temperature capability can be improved by the use of different materials and lubricants. Generally, the size of the bearings may be associated with the size of the rotor shaft. In other words, their size is dependent on the rotor shaft size. The bearings are susceptible to product contamination. Outboard bearings and inboard bearings are the two distinct configurations applied to a rotary valve’s endplates.
Operating Speed
Rotor speed determines the throughput rate. It is important to run the rotary valve at the correct speed to obtain maximum efficiency while meeting the required capacity. Rotor speed of a rotary airlock valve is generally determined with respect to bulk density and particle size of handled material, required throughput, pressure or vacuum level at inlet or outlet of the rotary valve and similar process data.
Drive System

This is the Worm gear reducer connection
This is the direct mounting of the gearbox to the rotor shaft of the valve. The drive system consists of the following; the gearbox, and the motor. The installation of the motor and the gear require less space.
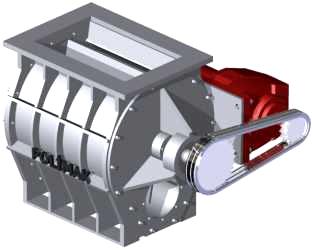
Chain gear connection
This is also known as a chain driven connection. The rotor and the gearbox are mounted on the side, driving the rotor shaft through a chain sprocket. This rotary valve drive system consists of a gearbox, chain, motor, guard, and sprockets. The sprocket size contributed to the speed of the system.

Direct coupling connection
This is a type of motor in which the load is connected directly to the motor. It consists of a shaft connecting a motor to a rotary valve. If there exists a mechanical coupling between the motor and the rotary valve along the shaft, then the drive system is known as a direct coupled drive or simply direct coupling. The coupling mechanism can either be a rigid one or a flexible one. Since the system has less parts, the energy dissipation is minimal.